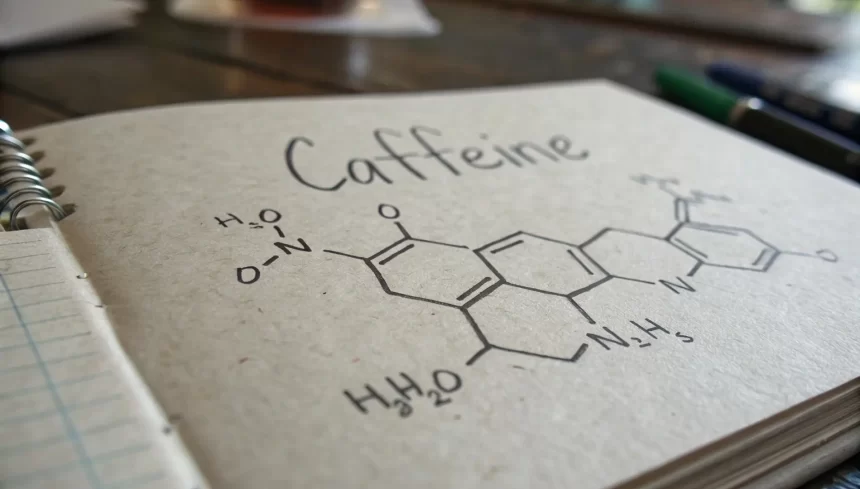
Caffeine is one of the most well-known and widely consumed stimulants in the world, playing a fundamental role in our daily lives. But caffeine is not just a way to stay awake. It has its own hidden properties and benefits, which you can learn about below.
- What is caffeine and how does it work?
- History
- How much of this substance can be used per day?
- Benefits of Caffeine
- Is it good or bad for the body?
- Who should avoid it?
- What are the symptoms of caffeine withdrawal?
- Does decaffeinated drink contain caffeine?
- Does this stimulant disturb your sleep at night?
- Does it affect athletic performance?
- How does it affect mental health?
- How is natural caffeine different from synthetic caffeine?
- Does it help with weight loss?
- Is this stimulant addictive?
- Are there caffeine-free boosters?
- Its effects on the elderly
- Conclusion
What is caffeine and how does it work?
Caffeine is a natural stimulant found in coffee beans, tea leaves, cocoa, and as an additive in soft drinks and energy drinks. It works by reducing adenosine, a chemical in your brain, making you feel less tired and more alert.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved caffeine for the treatment of apnea of prematurity.
History
The story of caffeine goes back thousands of years. When coffee was discovered by a shepherd named Kaldi in Ethiopia, he noticed that the sheep had more energy after eating coffee berries. From there, it spread to the Middle East, Europe, and eventually became a global phenomenon. Today, it is a $100 billion industry.
How much of this substance can be used per day?
Your response to this stimulant depends on factors like your body mass, overall health, and metabolism, and also varies depending on how used your body is to regular consumption. Experts recommend that you consume no more than 400 milligrams of caffeine per day (about four cups of coffee). Anything more than that can cause jitters, insomnia, or even heart palpitations.
Benefits of Caffeine
Caffeine doesn’t just keep you awake. It increases focus, improves mood, and even boosts memory. Athletes use it to perform better, and studies show it may help reduce the risk of certain diseases, such as Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s.
Is it good or bad for the body?
While it has various benefits such as improving alertness and increasing focus, consuming too much of it can have negative effects on your body and mind. High doses can lead to anxiety as it stimulates the central nervous system, increases heart rate, and makes you feel restless or jittery. Additionally, over time, regular use can lead to dependence.
Who should avoid it?
Pregnant women, people with heart disease, and those sensitive to caffeine. Even children and adolescents should limit their intake to avoid potential health risks.
There are currently no guidelines for its use in children. If children show signs of irritability, inability to sleep, sleep disruptions, or stomach upset, the stimulant should be reviewed.
If you are pregnant, limit your caffeine intake to 200 mg per day or less or avoid it altogether. Consuming large amounts of caffeine may increase the risk of miscarriage, difficult labor, and low birth weight.
What are the symptoms of caffeine withdrawal?
Headaches, fatigue, and irritability are common withdrawal symptoms when reducing or stopping this natural stimulant, especially if you have been using it regularly and heavily. These symptoms occur because your body has become accustomed to the stimulant’s effects, and when its levels decrease, it causes temporary disruptions in your brain chemistry. To minimize these symptoms, it should be tapered off gradually.
Does decaffeinated drink contain caffeine?
Decaf coffee is often touted as a caffeine-free option, but it’s not completely caffeine-free. A cup of decaffeinated coffee can still contain 2 to 5 milligrams of caffeine. A cup of coffee has about 95 milligrams of caffeine.
Does this stimulant disturb your sleep at night?
Caffeine can disrupt your sleep, especially if consumed too close to bedtime. This is because caffeine is a stimulant that blocks the action of adenosine, a brain chemical that causes drowsiness. Experts recommend cutting down on caffeine at least 6 hours before bed.
Does it affect athletic performance?
Many athletes use caffeine as a performance enhancer, relying on its ability to increase energy levels and improve athletic performance. When caffeine is consumed before exercise or physical activity, it stimulates the body’s nervous system, leading to increased alertness, focus, and a heightened sense of energy. This boost can help athletes fight fatigue, but the effects of caffeine can vary from person to person.
How does it affect mental health?
This stimulant affects different people differently, depending on factors such as genetics, tolerance, and sensitivity to the stimulant. For some people, caffeine can have positive effects, such as boosting mood and promoting a sense of alertness and well-being. However, in people who are more sensitive to caffeine, it may cause anxiety or palpitations. This is because caffeine stimulates the central nervous system, which can increase heart rate and make some people feel jittery.
How is natural caffeine different from synthetic caffeine?
Natural caffeine comes from plants like coffee and tea. While synthetic caffeine is made in laboratories and is often found in energy drinks. While they work similarly, some people prefer the natural stuff.
Does it help with weight loss?
Marketers often tout this ingredient as a weight loss aid because it temporarily increases metabolism and increases fat burning. Caffeine consumption increases heart rate and the release of certain hormones, such as adrenaline. This increase in adrenaline causes the body to break down fat cells and release fatty acids into the bloodstream. The body then uses these fatty acids as fuel for energy. As a result, it can temporarily increase the rate at which the body burns calories, a process known as thermogenesis.
In addition, it can enhance physical performance, allowing people to exercise harder and potentially burn more calories during their workout.
For effective and sustainable weight loss, it is much better to combine a healthy diet, regular physical activity, and lifestyle habits rather than relying on this stimulant or other stimulants.
Is this stimulant addictive?
Caffeine can be habit-forming. If you find it hard to function without your morning coffee, it may be a sign of dependence. While dependence on it is generally milder than other substances, it is still important to consume it in moderation to avoid potential problems.
Are there caffeine-free boosters?
- Boost your energy naturally with some herbal teas. Like peppermint or ginseng tea.
- Dehydration can lead to fatigue. So make sure you drink enough water throughout the day.
- Eat foods rich in natural sugars, such as fruits like bananas, apples, and oranges, which provide quick and sustained energy thanks to their vitamins, fiber, and natural sweetness.
- Walking or light stretching can stimulate blood flow, release endorphins, and make you feel more alert and energized.
Its effects on the elderly
As we age, our bodies’ ability to metabolize this substance decreases, and older people become more sensitive to its effects. This means it stays in the body’s system for longer, which can significantly affect their sleep.
In addition, this article can exacerbate anxiety in older people. Its stimulant properties can increase heart rate and restlessness, which may increase with age. This can lead to feelings of discomfort or even aggravate underlying conditions such as high blood pressure or arrhythmia.
Conclusion
Caffeine is a powerful and widely consumed stimulant with both benefits and drawbacks. While it can increase alertness and physical performance and even offer some health benefits, excessive consumption can lead to negative effects such as sleep disturbance, anxiety, or dependence. It is important to understand how your body reacts to it and consume it in moderation. For those who prefer not to consume this stimulant, there are natural alternatives to maintain energy and focus throughout the day.