Cardiologists are doctors who diagnose, treat, and manage heart disease. So a cardiologist plays an important role in keeping your heart healthy. Health insurance often covers visits to cardiologists, making it easier for patients to access the care they need.
Join us to learn about cardiologists, the warning signs of heart disease, and how to take good care of your heart.
- What do cardiologist do?
- Common Heart Diseases Treated by Cardiologists
- Types of Cardiologists
- Definitions of types of cardiologists
- Diagnostic Tests and Procedures Performed by Cardiologists
- What to Expect During Your First Cardiologist Visit
- Lifestyle Changes Recommended by Cardiologists
- What is the difference between cardiologists and other doctors?
- How Cardiologists Work with Other Medical Specialists
- Education to become a cardiologist
- When should you see a cardiologist?
- How Cardiologists Help Prevent Heart Disease?
- What you need to know when visiting a cardiologist
- Latest Advances in Cardiology
- Top Heart Centers in the United States
- Conclusion
Dr. Valentine Foster – Director of Mount Sinai Heart, New York “Cardiologists play a critical role in not only saving lives, but also in empowering patients to live longer, healthier lives. Our mission is about more than treatment; it’s about education and prevention.
What do cardiologist do?
To evaluate patients, cardiologists may perform physical exams and order various diagnostic tests, such as an electrocardiogram (EKG), blood tests, and stress tests to assess heart function. By analyzing these results, they can identify any underlying heart problems. Beyond diagnosis, cardiologists may prescribe medications and recommend lifestyle changes to support heart health, including a heart-healthy diet, regular physical activity, stress management, and weight control. In more complex cases, they may perform advanced procedures, such as pacemaker implantation or cardiac catheterization, to help improve heart function.
Common Heart Diseases Treated by Cardiologists
Cardiologists diagnose and treat a wide range of heart-related conditions. Some of the most common include:
- Coronary Artery Disease (CAD): Narrowing of the arteries due to plaque buildup, increasing the risk of heart attacks.
- Heart Failure: A condition where the heart cannot pump blood efficiently.
- Arrhythmias: Irregular heartbeats, such as atrial fibrillation.
- Hypertension (High Blood Pressure): A leading cause of heart disease and stroke.
- Valvular Heart Disease: Malfunctioning of heart valves, leading to conditions like aortic stenosis or mitral valve prolapse.
- Congenital Heart Defects: Structural heart abnormalities present at birth.
- Cardiomyopathy: Diseases of the heart muscle that affect its ability to pump blood.
- Pericarditis & Endocarditis: Infections or inflammation of the heart’s lining and valves.
Types of Cardiologists
While all cardiologists focus on the heart and blood vessels, many choose to specialize further within this field.
Here are some types of cardiologists:
– Clinical Cardiologist
– Heart Failure Specialist
– Pediatric Cardiologist
– Interventional Cardiologist
– Cardiac Specialist
– Congenital Cardiologist
– Cardiac Imaging Specialist
– Peripheral Cardiologist
– Preventive Cardiologist
– Cardiac Rehabilitation Specialist
– Electrophysiologist
– Geriatric Cardiologist
– Rheumatology Cardiologist
– Sports Cardiologist
– Cardiovascular Safety Specialist
Helen B. Taussig, pediatric cardiologist and founder of Pediatric Cardiology
“To keep children’s hearts healthy, we must advance with compassion and science to give them the opportunity to live full lives.”Definitions of types of cardiologists
Clinical Cardiologist:
Clinical cardiologists are specialists who provide comprehensive care for a wide variety of heart conditions, including coronary artery disease, arrhythmias, heart failure, and hypertension. They focus on diagnosing, treating, and managing heart disease through medication, lifestyle modifications, and other interventions as necessary.
Heart Failure Specialist:
These specialists concentrate on the diagnosis and treatment of heart failure, a condition where the heart struggles to pump blood effectively. They utilize advanced therapies such as medication management, device interventions (like pacemakers), and in some cases, heart transplants.
Pediatric Cardiologist:
Pediatric cardiologists are experts in diagnosing and treating heart conditions in children, ranging from congenital heart defects to acquired heart diseases. They provide care for infants, children, and adolescents with heart issues.
Interventional Cardiologist:
Interventional cardiologists specialize in the diagnosis and treatment of cardiovascular and structural heart conditions through minimally invasive catheter-based procedures. These include angioplasty, stent placement, and repairs for heart valve problems, following additional training beyond standard cardiology.
Cardiologist:
Cardiologists are medical doctors who focus on the diagnosis, management, and treatment of heart diseases, providing essential care for patients with heart conditions.
Congenital Cardiologist:
These specialists diagnose and treat heart conditions present from birth, managing both congenital heart defects and other related disorders in children and adults.
Cardiac Imaging Specialist:
Cardiac imaging specialists use advanced imaging techniques, such as CT scans, MRIs, and echocardiography, to assess and monitor the structure and function of the heart, aiding in diagnosis and treatment planning.
Peripheral Cardiologist:
Peripheral cardiologists focus on diseases affecting the arteries and veins outside the heart, particularly those of the arms, legs, and other peripheral regions, addressing conditions like peripheral artery disease.
Preventive Cardiologist:
Preventive cardiologists work with patients to reduce the risk of heart disease by managing risk factors such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, smoking, and obesity. They emphasize early detection and lifestyle changes to prevent cardiovascular issues.
Cardiac Rehabilitation Specialist:
These specialists design and oversee rehabilitation programs for patients recovering from heart surgery, heart attacks, or other cardiac events. Their role includes promoting recovery through exercise, education, and emotional support.
Electrophysiologist:
Electrophysiologists are experts in diagnosing and treating heart rhythm disorders (arrhythmias). They use procedures like electrophysiology studies, ablation, and device implantation (e.g., pacemakers or defibrillators) to correct abnormal heart rhythms.
Geriatric Cardiologist:
Geriatric cardiologists focus on heart health in older adults, addressing the unique challenges and conditions that arise in aging populations. They manage the treatment of heart diseases in elderly patients with consideration for other age-related health issues.
Cardiorheumatologist:
These specialists treat heart disease related to autoimmune conditions such as lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, and vasculitis. They manage the inflammatory effects of these diseases on heart health.
Sports Cardiologist:
Sports cardiologists specialize in cardiovascular care for athletes, assessing heart health, identifying exercise-related risks, and providing guidance on safe exercise regimens to prevent cardiac events in athletes.
Cardiovascular Safety Specialist:
Cardiovascular safety specialists work in clinical trial environments to monitor and manage cardiovascular risks associated with new drugs or medical devices. They ensure heart-related side effects are properly addressed during the development phase of these products.
Dr. Clyde Yancey – Chair of Cardiology at Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine
“In a world where heart disease is the leading cause of death, cardiologists are essential to advancing public health. Our work helps reduce risk, prevent sudden cardiac events, and ensure quality of life for millions.” Dr. Clyde Yancey – Chair of Cardiology at Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine
Diagnostic Tests and Procedures Performed by Cardiologists
Cardiologists use various tests to diagnose heart conditions. Some of the most common include:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG): Records electrical activity of the heart to detect arrhythmias or heart damage.
- Echocardiogram: An ultrasound of the heart that shows structure and function.
- Stress Test: Evaluates how the heart functions under exertion, often done on a treadmill or with medication.
- Cardiac Catheterization: A procedure where a thin tube is inserted into the heart to detect blockages.
- Holter Monitor: A portable ECG worn for 24-48 hours to track irregular heartbeats.
- Coronary Angiography: Uses dye and X-rays to visualize blood flow in the coronary arteries.
- MRI & CT Scans of the Heart: Provides detailed images of the heart’s structure.
What to Expect During Your First Cardiologist Visit
A first visit typically includes:
- Medical History Review: Discussion of symptoms, lifestyle, and family history.
- Physical Examination: Checking blood pressure, heart rate, and listening to heart sounds.
- Diagnostic Testing: The cardiologist may order an ECG, echocardiogram, or blood tests.
- Treatment Plan Discussion: Based on findings, the cardiologist may recommend lifestyle changes, medications, or further tests.
Lifestyle Changes Recommended by Cardiologists
Cardiologists emphasize lifestyle changes to support heart health:
- Healthy Diet: A Mediterranean or DASH diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats.
- Regular Exercise: At least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity activity per week.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight reduces heart disease risk.
- Stress Reduction: Techniques such as meditation, deep breathing, and yoga.
- Quitting Smoking & Limiting Alcohol: Avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol consumption significantly lowers heart risk.
What is the difference between cardiologists and other doctors?
Cardiologists specialize in diagnosing, treating, and managing diseases of the heart and blood vessels. Unlike general practitioners or internists who handle a broad range of health concerns, cardiologists receive extensive training focused on cardiovascular health. This expertise enables them to manage complex heart-related conditions, including heart attacks, heart failure, arrhythmias, and high blood pressure.
While other doctors conduct general health exams and treat common ailments, cardiologists use advanced diagnostic tools—such as electrocardiograms (EKG), echocardiograms, and stress tests—to assess heart function.
How Cardiologists Work with Other Medical Specialists
Heart health is closely linked to other conditions, so cardiologists often collaborate with:
- Primary Care Physicians: To manage overall health and coordinate care.
- Endocrinologists: To control diabetes and cholesterol, which impact heart health.
- Cardiac Surgeons: For cases requiring surgical interventions like bypass surgery.
- Nephrologists: To monitor kidney function, as kidney disease affects the heart.
- Pulmonologists: When heart disease is linked to lung conditions.
Education to become a cardiologist
Cardiologists undergo extensive training, starting with medical school before specializing in heart-related fields. Typically, a cardiologist completes a minimum of 10 years of medical education, which includes four years in medical school and three years of residency training. Afterward, they pursue an additional three years of specialized training in cardiology.
To become board-certified, they must also pass the cardiovascular disease exam administered by the American Board of Internal Medicine (ABIM).
When should you see a cardiologist?
You should see a cardiologist immediately if you see the following symptoms:
- Chest pain
- Dizziness
- Shortness of breath
- Flutter in the chest
- Fainting spells
- Rapid heartbeat or breathing
- Grayish color
- Heavy sweating
- Very low blood pressure or very slow heart rate
How Cardiologists Help Prevent Heart Disease?
Cardiologists focus on prevention by addressing risk factors early. Their approach includes:
- Risk Assessment: Checking cholesterol levels, blood pressure, family history, and lifestyle habits.
- Medication Management: Prescribing statins, beta-blockers, or blood thinners when necessary.
- Lifestyle Counseling: Providing guidance on diet, exercise, and smoking cessation.
- Monitoring & Early Intervention: Regular checkups help detect early signs of heart disease before it worsens.
What you need to know when visiting a cardiologist
When you see a cardiologist, your cardiologist will ask you questions about your symptoms and lifestyle to get a better understanding of your health. He or she may perform various tests to identify the problem. These tests help determine the overall health of your heart. After analyzing the test results, your cardiologist will diagnose any problems and recommend a treatment plan.
Latest Advances in Cardiology
The field of cardiology is evolving rapidly with new treatments and technologies:
- Minimally Invasive Heart Procedures: Techniques like TAVR (Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement) are revolutionizing valve replacement.
- Artificial Intelligence in Diagnosis: AI is being used to detect early signs of heart disease through imaging and ECG analysis.
- Wearable Heart Monitors: Smartwatches and other devices help track heart rhythms and detect irregularities.
- Personalized Medicine: Genetic testing is being used to tailor treatments to an individual’s specific risk factors.
- Regenerative Medicine: Stem cell therapy and tissue engineering are being explored for heart repair.
Top Heart Centers in the United States
1. Cleveland Clinic – Cleveland, Ohio
The Cleveland Clinic’s Cardiovascular and Thoracic Institute is frequently ranked as the leading heart center in the U.S., known for its innovative treatments and patient care.
2. Mayo Clinic – Rochester, Minnesota
The Mayo Clinic is widely recognized for its extensive heart care services, offering comprehensive treatment options and renowned expertise.
3. New York-Presbyterian/Columbia and Cornell Hospital – New York, New York
This East Coast facility is celebrated for its heart transplant program and interventional cardiology. It provides state-of-the-art treatments in a premier setting.
4. Cedars-Sinai Heart Institute – Los Angeles, California
As a top West Coast heart center, Cedars-Sinai is respected for its cardiovascular research and advanced treatment options.
5. Texas Heart Institute – Houston, Texas
Based at Baylor St. Luke’s Medical Center, the Texas Heart Institute is a prominent center for heart research and patient care.
6. Johns Hopkins Hospital – Baltimore, Maryland
Internationally acclaimed for cardiac care, Johns Hopkins specializes in both common and complex heart conditions, offering advanced cardiac and vascular surgical services.
Conclusion
A healthy heart is the cornerstone of a healthy life, so prioritizing your heart health is essential. Consulting a cardiologist to discuss your symptoms and lifestyle can help prevent heart issues and ensure you receive the proper treatment when needed. Keep in mind that simple changes—such as adopting a healthier lifestyle, staying active, and eating well—can have a significant impact on your heart’s well-being.
Make informed decisions to protect your heart and live a longer, healthier life.









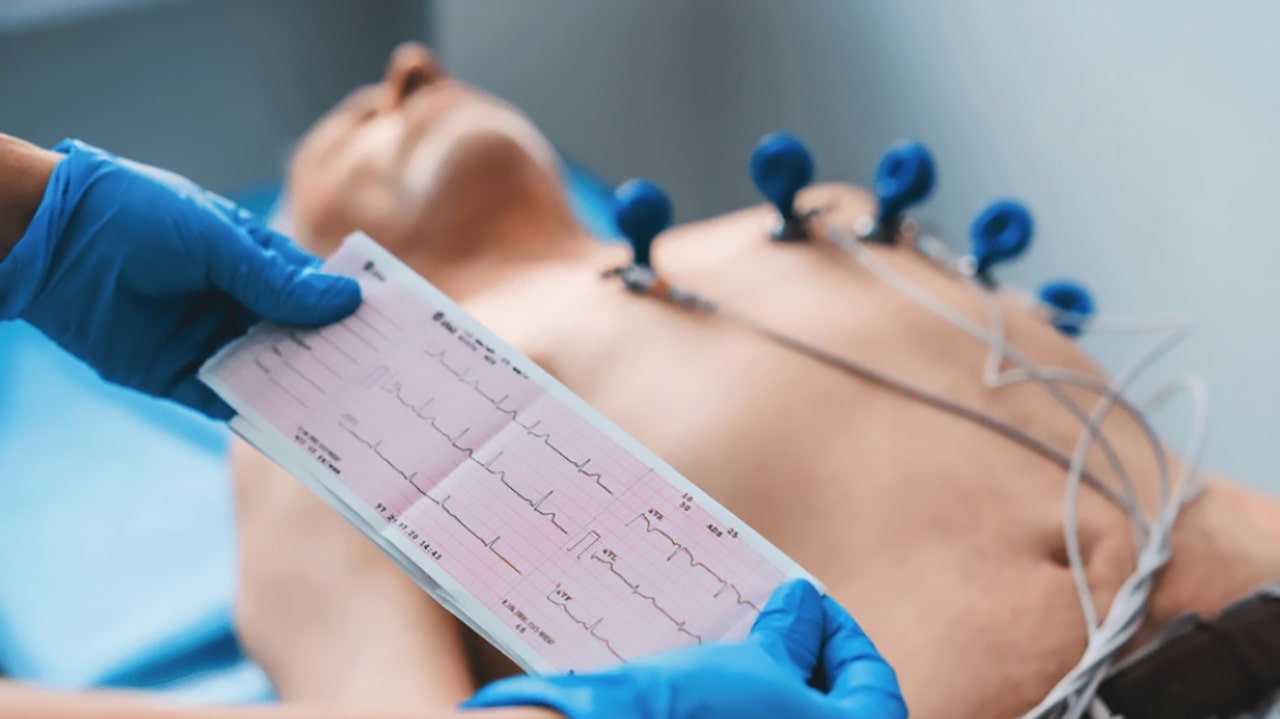







Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.